| Problem 1 |
| circuit_city > Write a SELECT statement to display the number of items sold as shown. Escriba un comando SQL para mostrar el número de artículos que se han vendido como se muestra. |

| Problem 2 |
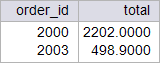
| circuit_city > Write a SELECT statement to display the total cost of orders 2000 and 2003. Escriba un comando SQL para mostrar el costo total de las órdenes 2000 y 2003. |
| Problem 3 |
| circuit_city > Write the total_cost function to compute the total cost of an order. The function takes the order_id and returns the total cost of the order. Using: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. Cree la función total_cost para calcular el costo de una orden dado el orden_id. Usando: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
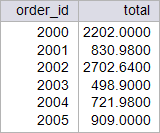
| SQL> connect circuit_city Enter password: Connected. SQL> SELECT order_id, 2 total_cost(order_id) AS total 3 FROM orderx; ORDER_ID TOTAL ---------- ---------- 2000 2202 2001 830.98 2002 2702.64 2003 498.9 2004 721.98 2005 909 6 rows selected. |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| SELECT order_id, dbo.total_cost(order_id) AS total FROM orderx; |
| Problem 4 |
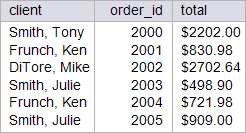
| circuit_city > Write a SELECT statement to display the total cost of each order as shown. Use the total_cost function that was previously created. Using: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. Escriba un comando SQL para mostrar el costo total de cada una de las órdenes como se muestra. Use la función total_cost que fue creada previamente. Usando: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| CLIENT ORDER_ID TOTAL -------------------- ---------- ------------ Smith, Tony 2000 $2,202.00 Smith, Julie 2005 $909.00 Smith, Julie 2003 $498.90 DiTore, Mike 2002 $2,702.64 Frunch, Ken 2004 $721.98 Frunch, Ken 2001 $830.98 6 rows selected. |
| Problem 5 |
| circuit_city > Write a SELECT statement to display the total number of items sold with an item_id between 104 and 110. Escriba un comando SQL para mostrar el número total de artículos vendidos que tienen item_id entre 104 y 110. |
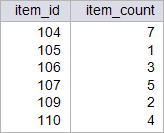
| Problem 6 |
| circuit_city > Write a function called sold to compute the number of items sold. The function takes the item_id and returns the number of items sold. Use SUM, GROUP BY or HAVING in your function. Using: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. Escriba una función llamada sold para calcular el número total de artículos vendidos que tienen un item_id dado. Use en su función: SUM, GROUP BY o HAVING.Usando: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| SQL> SELECT item_id, 2 sold(item_id) AS sold 3 FROM item; ITEM_ID SOLD ---------- ------------- 100 4 101 102 7 103 4 104 7 105 1 106 3 107 5 108 109 2 110 4 111 12 12 rows selected. |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| SELECT item_id, dbo.sold(item_id) AS sold FROM item; |
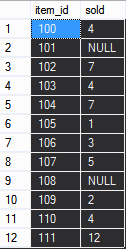
| Problem 7 |
| circuit_city > Write a SELECT statement to display the item name and the quantity sold of that item. Use the sold function previously implemented. Using: (a) Oracle, (b) Microsoft SQL Server. Escriba un comando SQL para mostrar el número total de artículos con sus nombres. Use la función sold que se implementó previamente. Usando: (a) Oracle, (b) Microsoft SQL Server. |
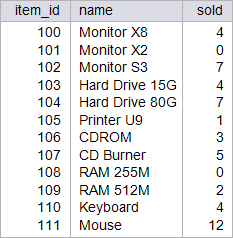
| Problem 8 |
| circuit_city > Create the soldn function to compute the total number of items sold given an item_id (same as the sold function) but without using SUM, GROUP BY nor HAVING in the function implementation. Using: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. Cree la función soldn para calcular el número total de artículos vendidos dado un item_id (lo mismo que la función sold) pero sin usar SUM, GROUP BY ni HAVING en la implementación de la función. Usando: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| SQL> SELECT item_id, 2 soldn(item_id) AS sold 3 FROM item; ITEM_ID SOLDN ---------- ---------- 100 4 101 0 102 7 103 4 104 7 105 1 106 3 107 5 108 0 109 2 110 4 111 12 12 rows selected. |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| SELECT item_id, name, dbo.soldn(item_id) AS sold FROM item; |
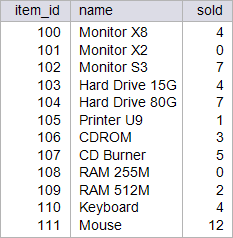
| Tip |
| The main difference between the sold function and the soldn function is that the sold function returns NULL when no item has been sold, and soldn returns zero. La diferencia principal entre la función sold y la función soldn es que la función sold regresa NULL cuando el artículo no se ha vendido, mientras que la función soldn regresa cero. |
| Problem 9 |
| circuit_city > Write a SELECT statement using the sold function previously implemented to display the name of the item: (a) most popular, (b) least sold. Note that if you use the soldn function, the query returns the item that has never been sold, on the other hand, if you use the sold function, the query returns the item that has been sold the minimum number of times. Usando la función sold previamente implementada escriba una consulta SQL para mostrar el nombre (a) del artículo más vendido, (b) el artículo menos vendido. Note que si usted usa la función soldn, la consulta regresa el artículo que nunca se ha vendido, por otro lado, si usted usa la función sold, la consulta regresa el artículo menos vendido. |
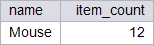
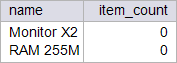
| Problem 10 |
| circuit_city > Write a SELECT statement using the sold function previously implemented to display the name of the most popular item and the least sold. Usando la función sold previamente implementada escriba una consulta SQL para mostrar el nombre del artículo más vendido y del menos vendido. |
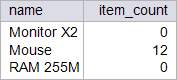
| Problem 11 |
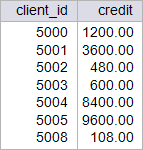
| circuit_city > Write a stored procedure called p_creinc to increase 20 % the credit of all the clients, use CURSOR. This procedure will destroy the original data from the client_credit Table. Restore the database to its original data by running your setup scripts after completion of this problem. Using: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. Escriba un procedimiento almacenado llamado p_creinc para incrementar en 20% el crédito de todos los clientes, Use CURSOR. Este procedimiento destruirá los datos originales de la tabla client_credit. Al término de esta actividad no se olvide de restaurar los datos originales de la base de datos. Usando: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| SQL> SELECT client_id, 2 credit 3 FROM credit_client; CLIENT_ID CREDIT ---------- ---------- 5000 1000 5001 3000 5002 400 5003 500 5004 7000 5005 8000 5008 90 7 rows selected. SQL> EXECUTE p_creinc; PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. SQL> SELECT client_id, 2 credit 3 FROM credit_client; CLIENT_ID CREDIT ---------- ---------- 5000 1200 5001 3600 5002 480 5003 600 5004 8400 5005 9600 5008 108 7 rows selected. |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| SELECT client_id, credit FROM credit_client; |
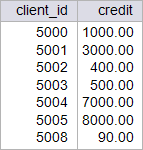
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| USE circuit_city; EXECUTE p_creinc; |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| SELECT client_id, credit FROM credit_client; |
| Problem 12 |
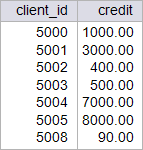
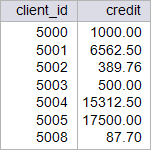
| circuit_city > Write a stored procedure call p_promo118 to increase 118.75 % the credit of clients if their current credit is more than 2000, and reduce the credit by 2.56 % if their current credit is less than 500. This procedure will destroy the original data from the credit_client table. Restore the database to its original data by running your setup scripts after completion of this problem. Using: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. Escriba un procedimiento almacenado llamado p_promo118 para incrementar en 118.75% el crédito de los clientes, si su credito actual es mas de 2000, y reducir el credito por 2.56%, si el credito actual es menor a 500. Este procedimiento destruirá los datos originales en la tabla credit_client. Restaure la base de datos con sus datos originales al terminar el problema. Usando: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| SQL> SELECT client_id, credit FROM credit_client; CLIENT_ID CREDIT ---------- ---------- 5000 1000 5001 3000 5002 400 5003 500 5004 7000 5005 8000 5008 90 7 rows selected. SQL> EXECUTE p_promo118; PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. SQL> SELECT client_id, credit FROM credit_client; CLIENT_ID CREDIT ---------- ---------- 5000 1000 5001 6562.5 5002 389.76 5003 500 5004 15312.5 5005 17500 5008 87.7 7 rows selected. |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| SELECT client_id, credit FROM credit_client; |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| USE circuit_city; EXECUTE p_promo118; |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| SELECT client_id, credit FROM credit_client; |
| Problem 13 |
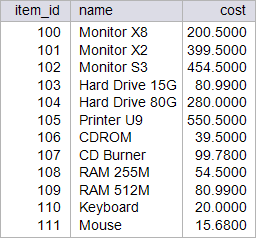
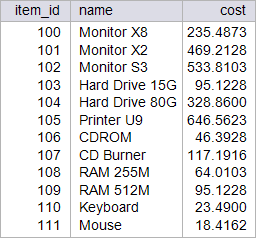
| circuit_city > Write a stored procedure called p_sales1745 to increase 17.45 % the cost of all the items in the item table. This procedure will destroy the original data from the item Table. Restore the database to its original data by running your setup scripts after completion of this activity.. Using: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. Escriba un procedimiento almacenado llamado p_sales1745 para incrementar en 17.45% el costo de todos los artículos en la tabla item. Este procedimiento destruirá los datos originales en la tabla item. Restaure la base de datos con sus datos originales al terminar el problema. Usando: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| SQL> SELECT item_id, name, cost 2 FROM item; ITEM_ID NAME COST ---------- --------------- ---------- 100 Monitor X8 200.5 101 Monitor X2 399.5 102 Monitor S3 454.5 103 Hard Drive 15G 80.99 104 Hard Drive 80G 280 105 Printer U9 550.5 106 CDROM 39.5 107 CD Burner 99.78 108 RAM 255M 54.5 109 RAM 512M 80.99 110 Keyboard 20 ITEM_ID NAME COST ---------- --------------- ---------- 111 Mouse 15.68 12 rows selected. SQL> EXECUTE p_sales1745; PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. SQL> SELECT item_id, name, cost 2 FROM item; ITEM_ID NAME COST ---------- --------------- ---------- 100 Monitor X8 235.49 101 Monitor X2 469.21 102 Monitor S3 533.81 103 Hard Drive 15G 95.12 104 Hard Drive 80G 328.86 105 Printer U9 646.56 106 CDROM 46.39 107 CD Burner 117.19 108 RAM 255M 64.01 109 RAM 512M 95.12 110 Keyboard 23.49 111 Mouse 18.42 12 rows selected. |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| SELECT item_id, name, cost FROM item; |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| USE circuit_city; EXECUTE p_sales1745; |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| SELECT item_id, name, cost FROM item; |
| Problem 14 |
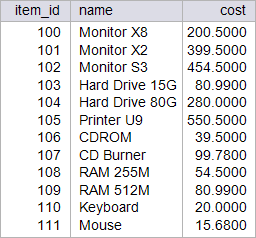
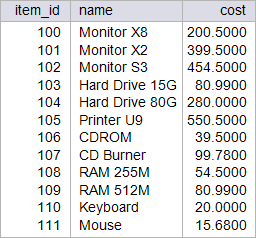
| circuit_city > Write a stored procedure called p_spring to increase by 12.55 % the cost of those items that cost more than 300 dollars, and reduce by 25% the cost of those items that are cheaper than 100 dollars from the item table. This procedure will destroy the original data from the item Table. Restore the database to its original data by running your setup scripts after completion of this activity. Using: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. Escriba un procedimiento almacenado llamado p_spring para incrementar en 12.55% el costo de todos los artículos en la tabla item que cuestan mas de 300 dólares, y reducir en 25% el costo de aquellos artículos que cuestan menos de 100 dólares. Este procedimiento destruirá los datos originales en la tabla item. Restaure la base de datos con sus datos originales al terminar el problema. Usando: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| SQL> SELECT item_id, name, cost FROM item; ITEM_ID NAME COST ---------- --------------- ---------- 100 Monitor X8 200.5 101 Monitor X2 399.5 102 Monitor S3 454.5 103 Hard Drive 15G 80.99 104 Hard Drive 80G 280 105 Printer U9 550.5 106 CDROM 39.5 107 CD Burner 99.78 108 RAM 255M 54.5 109 RAM 512M 80.99 110 Keyboard 20 111 Mouse 15.68 12 rows selected. SQL> EXECUTE p_spring; PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. SQL> SELECT item_id, name, cost FROM item; ITEM_ID NAME COST ---------- --------------- ---------- 100 Monitor X8 200.5 101 Monitor X2 449.64 102 Monitor S3 511.54 103 Hard Drive 15G 60.74 104 Hard Drive 80G 280 105 Printer U9 619.59 106 CDROM 29.63 107 CD Burner 74.84 108 RAM 255M 40.88 109 RAM 512M 60.74 110 Keyboard 15 111 Mouse 11.76 12 rows selected. |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| SELECT item_id, name, cost FROM item; |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| USE circuit_city; EXECUTE p_spring; SELECT item_id, name, cost FROM item; |
| Problem 15 |
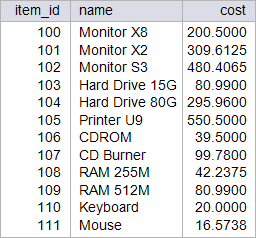
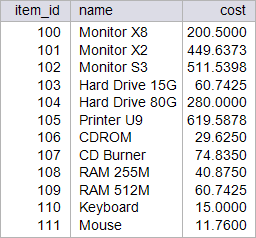
| circuit_city > Write a stored procedure called p_winter to increase by 5.7 % the cost of those items which sold quantity is more than 5, and to reduce the price by 22.5% the cost of those items that have never been sold. This procedure will destroy the original data from the item Table. Restore the database to its original data by running your setup scripts after completion of this activity. Using: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. Escriba un procedimiento almacenado llamado p_winter para incrementar en 5.7% el costo de aquellos artículos que se han vendido una cantidad de más de cinco, y reducir el costo en un 22.5% el costo de aquellos artículos que nunca se han vendido. Este procedimiento destruirá los datos originales en la tabla item. Restaure la base de datos con sus datos originales al terminar el problema. Usando: (a) Oracle. (b) Microsoft SQL Server. |
| MSDOS: cmd.exe |
| SQL> SELECT item_id, name, cost FROM item; ITEM_ID NAME COST ---------- --------------- ---------- 100 Monitor X8 200.5 101 Monitor X2 399.5 102 Monitor S3 454.5 103 Hard Drive 15G 80.99 104 Hard Drive 80G 280 105 Printer U9 550.5 106 CDROM 39.5 107 CD Burner 99.78 108 RAM 255M 54.5 109 RAM 512M 80.99 110 Keyboard 20 111 Mouse 15.68 12 rows selected. SQL> EXECUTE p_winter; PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. SQL> SELECT item_id, name, cost FROM item; ITEM_ID NAME COST ---------- --------------- ---------- 100 Monitor X8 200.5 101 Monitor X2 309.61 102 Monitor S3 480.41 103 Hard Drive 15G 80.99 104 Hard Drive 80G 295.96 105 Printer U9 550.5 106 CDROM 39.5 107 CD Burner 99.78 108 RAM 255M 42.24 109 RAM 512M 80.99 110 Keyboard 20 111 Mouse 16.57 12 rows selected. |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| SELECT item_id, name, cost FROM item; |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| USE circuit_city; EXECUTE p_winter; |
| Microsoft SQL Server |
| SELECT item_id, name, cost FROM item; |